Business Analytics brings together two incredibly significant terms: business and analytics. Each term plays a vital role. Analytics, for instance, is the process utilising:
- Statistical Techniques (central tendency measures, graphs, and so forth): These tools help in summarising data to derive meaningful insights, enabling business analysts to identify patterns, trends, and potential outliers within large datasets. Graphs and central tendency measures aid in visualising data, making complex information easier to interpret and understand.
- Information System Software (data mining, sorting routines): Information system software, such as data mining and sorting routines, is integral to Business Analytics. This software help unearth hidden patterns and correlations in big data, thereby supporting analysts in making accurate predictions, categorising data, and making informed business decisions.
- Operations Research Methodologies (such as linear programming): Operations research methodologies, including linear programming, assist business analysts in making optimal decisions by utilising mathematical and computational models. Such methods are useful in resource allocation, scheduling, transportation, and other business logistics to maximise efficiency or minimise costs.
Functions served by analytics include exploring, visualising, discovering, and communicating patterns or trends in data. Keeping these crucial functions in mind, we can define Business Analytics (BA) as a process starting with business-related data collection, followed by the sequential application of descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive major analytic components.
The Rising Demand for Business Analytics Skills
Opportunities for business analysts have boomed as more and more organisations adopt data-driven and technology-focused approaches. Business Analytics is implemented across various industries, including but not limited to Automotive, Health Care, Media, Banking, Retail, Sports Analytics, and Manufacturing.
The outcome of applying Business Analytics is clear: it supports business decision-making and significantly enhances organisational performance.
Business Analytics has the potential to resolve all problem areas hindering the growth of an enterprise. For instance, a recent survey explored the relevance of Business Analytics in streamlining organisational function, and the results were indeed enlightening.
The Value of Business Analytics Expertise

Business Analytics expertise is in short supply – it’s ranked second in a Computerworld survey on the most challenging skills to find. McKinsey Global Institute reports that the United States could face a shortage of between 140,000 and 190,000 individuals with deep Business Analytics skills, plus an additional 1.5 million managers equipped to implement the results.
So, embarking on a career in Business Analytics might be a very wise move. Examples of Business Analytics jobs include:
- BA Strategy Consultants: As more businesses realise the power of data, BA Strategy Consultants are poised for a surge in demand. They will play pivotal roles in steering strategic decisions, driving business growth and increasing competitive advantage by leveraging data insights.
- Business Intelligence and Performance Management Consultants: As organisations increasingly lean towards data-driven decision-making, Business Intelligence and Performance Management Consultants will be instrumental. Their ability to utilise business intelligence tools to enhance organisational performance and competitiveness is expected to see a steep growth trajectory.
- Advanced Analytics and Optimization Consultants: With the explosion of data and businesses’ increasing reliance on it, Advanced Analytics and Optimization Consultants will be sought after more than ever. Their role in deriving deep insights from data and optimising business operations will be vital in shaping future business strategies.
and many more.
Key Skills for Business Analytics
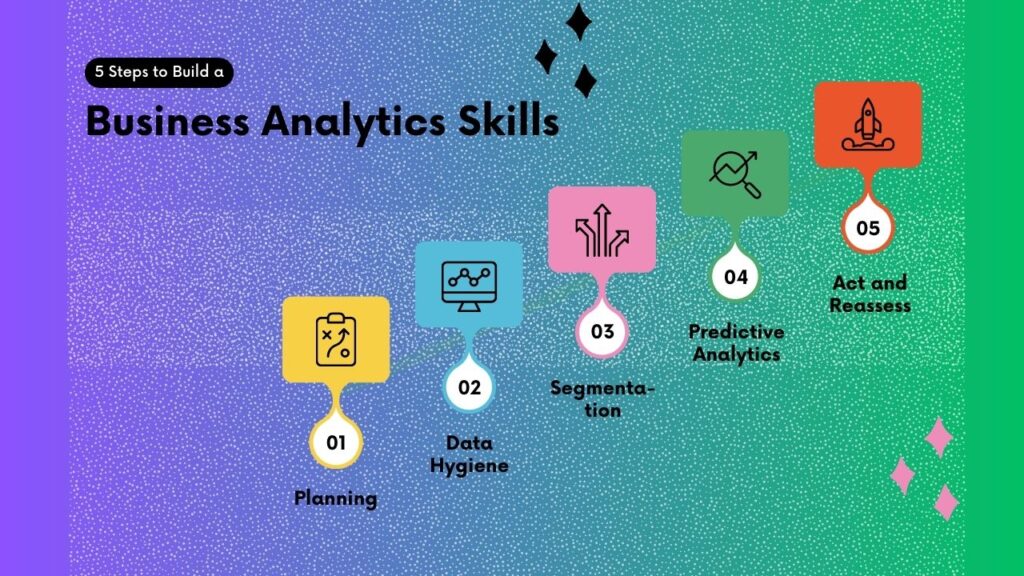
In order to thrive in a Business Analytics role, certain personal skills are needed. These include:
- An Analytical Mind: A Business Analyst needs an analytical mind to comprehend and interpret data, identify trends, and make data-driven recommendations. This ability to think analytically is at the heart of sound decision-making.
- A Problem-Solving Attitude: Business Analysts often deal with complex situations and challenges. A problem-solving attitude allows them to identify issues, consider possible solutions, and select the best course of action, ultimately improving business outcomes.
- Excellent Communication Skills: Business Analysts serve as a bridge between different stakeholders. Their role necessitates clear and concise communication to translate complex data findings into understandable and actionable insights for decision-makers.
- The Ability and Interest to Conduct and Analyse Survey Findings: Conducting and analysing surveys enables Business Analysts to gather valuable data directly from consumers or employees. This skill is key to understanding market trends, customer behaviours, or employee satisfaction.
- The Capability to Manage Vast Data Sets: As businesses generate immense volumes of data daily, Business Analysts need the capability to manage these vast data sets. They should be able to organise, interpret, and use this data to draw valuable conclusions.
- An Inquisitive Nature to Solve Complex Problems: An inquisitive nature helps Business Analysts to question the status quo, dig deeper into issues, and uncover root causes. This curiosity is vital to problem-solving and innovation.
One must also have:
- Refined Interpretation Skills: Business Analysts need to interpret data accurately and make sense of numbers, statistics, and trends. These refined interpretation skills are essential to converting raw data into meaningful insights.
- A Keen Interest in Technology: Given the tech-driven nature of data analysis, a Business Analyst’s interest in technology is vital. They need to understand and leverage modern technologies, data tools, and software to enhance their data analysis capabilities.
- A Drive for In-depth Research: In-depth research skills enable Business Analysts to explore market trends, competitor strategies, and consumer behaviour. This drive for research is essential for making informed, effective business strategies.
- The Ability to Work Well Within a Team: Business Analysts frequently collaborate with various teams and departments. Their ability to work well within a team, respecting and understanding different viewpoints, ensures smooth project execution and a more cohesive working environment.
The Wide Range of Business Analytics Applications
Business Analytics has a broad range of applications and usages. It is used for:
- Descriptive Analysis: Business analysis helps with descriptive analysis by turning raw data into a clear understanding of past and present situations. It allows businesses to identify trends, patterns, and draw conclusions based on factual data.
- Predictive Analysis: Through predictive analysis, business analysis utilises historical data to forecast future outcomes. It allows businesses to anticipate future trends and make proactive, data-driven decisions.
- Prescriptive Analysis: In prescriptive analysis, business analysis identifies the best course of action for a given situation. It aids in developing optimization techniques, enabling businesses to improve operations, increase efficiency, and enhance overall business performance.
Career Prospects after an MBA in Business Analytics
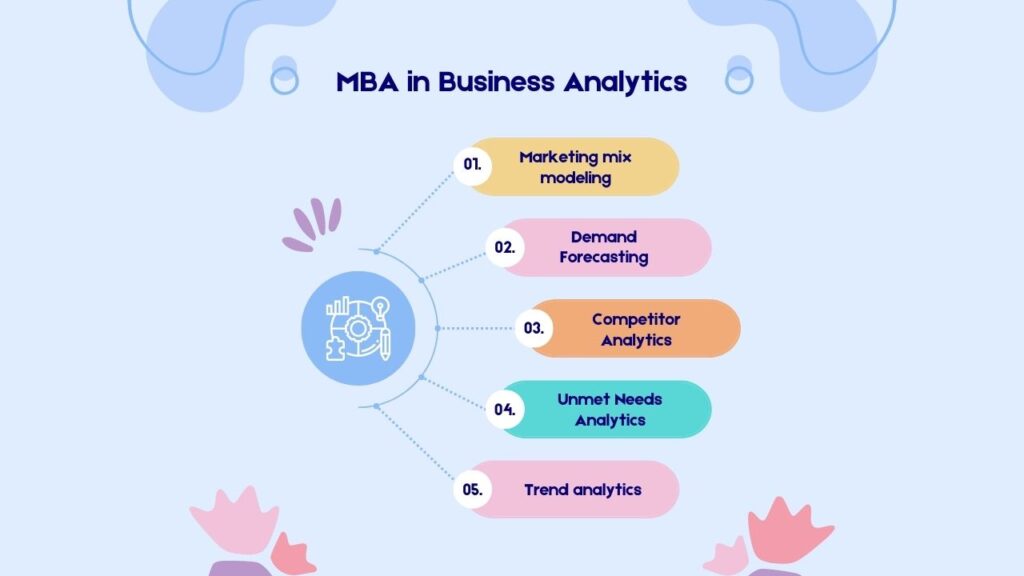
There are numerous exciting career paths available after obtaining an MBA in Business Analytics. These include roles as:
- Business Analyst: An MBA in Business Analytics equips individuals with the essential knowledge and skills to understand business needs and translate them into data-driven solutions. As companies continue to realise the value of data, Business Analysts will see robust demand, making this a promising career path.
- Data Analyst: This degree provides a solid foundation in statistical techniques, data mining, and handling large datasets—essential skills for a Data Analyst. With more companies leveraging data to drive decision-making, the prospects for Data Analysts are bright and growing.
- Data Scientist: An MBA in Business Analytics can introduce the advanced data processing and machine learning techniques needed by Data Scientists. Data Scientists, often termed ‘the sexiest job of the 21st century,’ have an incredibly promising career outlook due to the increasing reliance on data across all industries.
- Predictive Modeller: The program equips students with skills in predictive analytics, a key requirement for Predictive Modellers. As businesses increasingly aim to anticipate future trends, the demand for Predictive Modellers is expected to rise considerably.
- Market Research Analyst: The degree can develop a strong understanding of market trends and consumer behaviour, essential for Market Research Analysts. The constant need for companies to understand their market and customers ensures a bright future for these professionals.
- Business Intelligence Expert: An MBA in Business Analytics offers a comprehensive understanding of business intelligence tools and applications, preparing individuals for a career as a Business Intelligence Expert. With businesses striving to make more informed decisions, the demand for these experts is poised for strong growth.
- Data Mining Expert: The program provides knowledge of data mining techniques and software, crucial for a Data Mining Expert. As more businesses seek to unearth valuable insights from their data, the prospects for Data Mining Experts will continue to be favourable.
among others.
With the world’s ever-increasing reliance on data and the importance of having the right information available at the right time, Business Analytics is quickly becoming a sought-after field of knowledge. It’s an excellent choice for career enhancement.
If you’re planning to lead an organisation or department successfully in the future, then Business Analytics skills are essential tools in your professional toolkit.

