
Cloud computing is a cornerstone of modern technology. The cloud is rapidly transforming how businesses operate, and organisations require skilled professionals who can navigate this new landscape. BCA and MCA students must understand its principles and applications to excel in their future careers.
This article talks about a fundamental aspect of cloud computing – deployment models. Knowing the differences between public, private, and hybrid cloud computing deployment models allows you to make informed decisions when building or managing IT infrastructure. This knowledge will prove valuable to you in various career paths (from application development to system administration).
If you can recommend the most secure and cost-effective cloud solution for a client, you will always be in demand in the job market!
What is Cloud Computing? Why Deployment Models Matter?

Cloud computing has revolutionised the way we store, process, and access data. It involves delivering computing resources like servers, databases, and software over the internet. It offers advantages like:
- Scalability: Easily adjusting resources to meet demand,
- Cost-effectiveness: Eliminating upfront hardware costs,
- Accessibility: Accessible from anywhere with a connection, and
- Reliability: Thanks to provider-maintained infrastructure.
These advantages give you a competitive edge as cloud adoption becomes widespread across industries.
Choosing the right deployment model (public, private, or hybrid) is essential for maximising the benefits of cloud computing. Public clouds offer shared resources, making them cost-effective. Private clouds deliver dedicated resources for enhanced security and control. Hybrid clouds provide the flexibility of both worlds.
Factors like security needs, desired cost control, flexibility requirements, and regulatory compliance should all play a role in your deployment model decision. Understanding these nuances will make you a valuable asset in the tech industry as businesses navigate the complexities of cloud computing.
Understanding Deployment Models in Detail
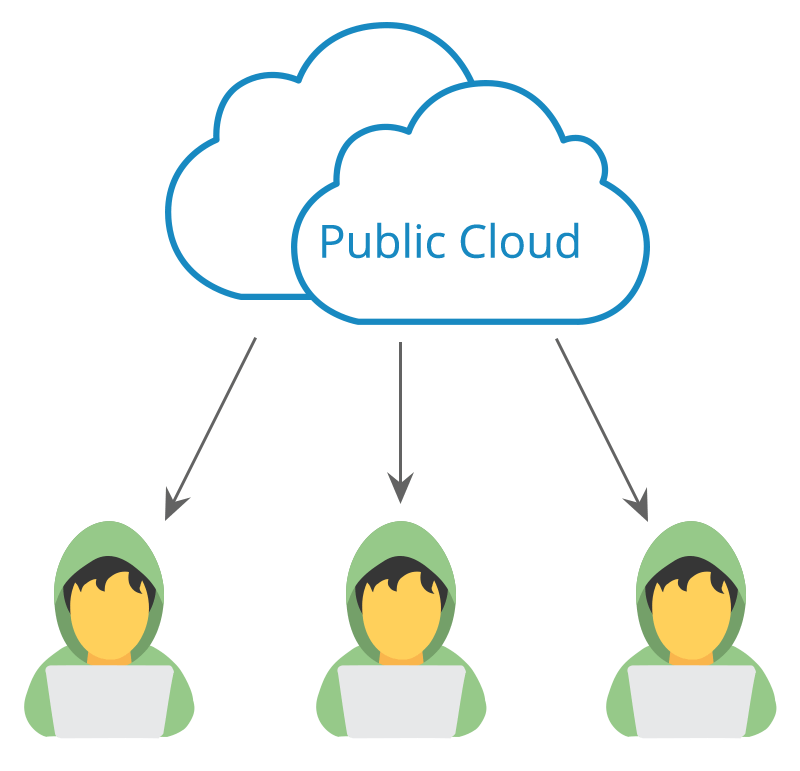
1. Public Cloud:
In a public cloud, computing resources (servers, storage, etc.) are owned and operated by a cloud service provider and shared among multiple customers. Think of it as renting space in a large, shared data centre. You only pay for the resources you use, making it a cost-effective option for variable workloads.
Examples of Public Cloud Providers
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): A comprehensive suite of cloud services, popular for its vast array of options.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Known for its strengths in data analytics and artificial intelligence.
- Microsoft Azure: Offers seamless integration with other Microsoft products and services.
Typical Use Cases for Public Clouds
- Website Hosting: Public clouds are ideal for hosting websites and web applications, especially those with unpredictable traffic patterns.
- Development Environments: Developers can quickly spin up test environments without the need for dedicated hardware.
- Data Storage: Public clouds provide an easy and scalable way to store non-sensitive data or backups.
The public cloud model offers scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of access, making it an attractive starting point for many organisations and a great tool for BCA and MCA students to experiment with. As you continue your studies, keep in mind that other deployment models, like private cloud or hybrid cloud, offer different advantages that may be better suited for specific needs.
2. Private Cloud:
A private cloud is a cloud environment where computing resources are used exclusively by a single organisation. This means the hardware and software aren’t shared with any other customers. If you go for the on-premises deployment option, the organisation owns and manages the hardware within its own data centre.
If you choose the third-party management deployment option, a cloud provider manages dedicated resources for the organisation, potentially in an off-site location.
Examples of Private Cloud Solutions
- Self-managed: Using technologies like OpenStack or VMware to build your own private cloud.
- Managed Solutions: Options like Microsoft Azure Stack allow for consistency with Azure services while retaining exclusive control.
Ideal Use Cases for Private Clouds
- Highly Sensitive Data: Organisations handling confidential financial or healthcare data often opt for enhanced security and control of a private cloud.
- Strict Regulatory Requirements: Industries like government or finance may have mandates that a private cloud can help meet.
- Need for Customisation: If an organisation has unique workloads or specific performance demands, the flexibility of a private cloud can be invaluable.
While private clouds can involve higher setup and management costs, they provide unmatched levels of security, compliance, and customisation. For BCA and MCA students aiming for roles in network administration, IT security, or heavily regulated industries, understanding private cloud architecture and implementation will be a significant asset.
3. Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is a model that strategically integrates both public and private cloud environments. This allows organisations to leverage the strengths of each while addressing specific needs and constraints.
Example: Leveraging the Hybrid Approach
Let’s talk about a company that stores sensitive customer data on a private cloud for security compliance. However, they occasionally face spikes in traffic, like seasonal sales events.
Instead of investing in additional on-premise infrastructure, they can “burst” into the public cloud, handling the increased workload while maintaining control over their core data.
Key Use Cases for Hybrid Clouds
- Cost Optimisation: Routine workloads can run on a cost-effective private cloud while leveraging the public cloud’s scalability for peak demand.
- Enhanced Flexibility: Organisations can move workloads between public and private clouds as needed for performance, security, or compliance reasons.
- Managing Control: A hybrid approach allows granular control over where sensitive data is stored while retaining the option for less sensitive applications to run in the public cloud.
A hybrid cloud allows for a nuanced approach to cloud computing. As BCA and MCA students, understanding how to design and manage hybrid solutions will broaden your skillset. As businesses demand adaptability and efficiency, being able to architect hybrid cloud solutions will set you ahead in the IT industry.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Computing Deployment Model?

Some of the key considerations while choosing the best cloud computing deployment model for an organisation are:
1. Security Requirements:
How sensitive is the data you’ll be handling? Private clouds offer the highest level of security and control, ideal for confidential or regulated information.
2. Cost Sensitivity:
Public clouds excel with pay-as-you-go models, making them cost-effective for variable workloads. Private clouds can involve higher upfront costs but may offer better long-term cost control.
3. Need for Customisation:
Does your organisation have unique software or hardware requirements? Private clouds provide maximum flexibility to tailor the environment to your specific needs.
4. Scalability Needs:
Do you experience traffic spikes or anticipate rapid growth? Public clouds offer virtually unlimited scalability, while hybrid clouds can provide “burst” capacity.
5. Regulatory Compliance:
Does your industry have strict data storage or privacy regulations? A private or hybrid cloud may be necessary to adhere to specific compliance standards.
Decision-Making Framework for Cloud Computing Deployment Models
| Key Consideration | Questions to Ask | Cloud Model(s) to Consider |
| Data Sensitivity | How sensitive is the data (confidential, regulated)? | Private Cloud (Highest security) |
| Cost Sensitivity | Is upfront cost a major concern? Do you have variable workloads? | Public Cloud (Pay-as-you-go) |
| Customization Needs | Do you have unique software or hardware requirements? | Private Cloud (Maximum flexibility) |
| Scalability & Growth | Do you anticipate traffic spikes or rapid growth? | Hybrid Cloud (Scalable while customizable), Public Cloud (Fast scaling) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Are there strict data storage or privacy regulations? | Private or Hybrid Cloud (May be required for compliance) |
Real-World Examples
Public Cloud:
- Netflix: A prime example of leveraging public cloud (AWS) for scalability. Their streaming service seamlessly handles massive fluctuations in user demand.
- Dropbox: Built their file storage and sharing platform on public cloud infrastructure, allowing them to focus on their core service rather than managing hardware.
Private Cloud:
- Healthcare Providers: Hospitals often favour private clouds to safeguard extremely sensitive patient data and adhere to HIPAA regulations.
- Financial Institutions: Banks may utilise private clouds to meet strict security and compliance standards while maintaining control over their core systems.
Hybrid Cloud:

- Retailers: A retailer might maintain inventory management systems on a private cloud, while their e-commerce website runs on the public cloud to handle seasonal traffic surges.
- Development Teams: Software development teams can utilise a hybrid approach, keeping sensitive code in a private cloud while using public cloud resources for testing and staging environments.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is a transformative force shaping the modern technological landscape. For BCA and MCA students, understanding cloud deployment models opens pathways to exciting career opportunities. By grasping the distinctions between public, private, and hybrid clouds, you gain the ability to design secure, scalable, and cost-effective solutions for the ever-evolving needs of businesses.
Whether it’s a multinational corporation seeking the flexibility of a hybrid model or a healthcare provider prioritising the security of a private cloud, your expertise in cloud deployment strategies will surely make you a sought-after asset. Since the world is increasingly dependent on the cloud, your ability to navigate this domain will secure your success in the tech industry.

