
With the huge rise in speed and connection that comes with the transition from 5G to 6G networks, our daily lives will likely go through never before seen changes. As the 5G era begins, conversations are already starting to take place concerning 6G networks and how, by 2030 or so, they will change both technology and society. Our mobile experience will be improved by making the switch from 5G to 6G networks, which will also empower many sectors and open up previously unimaginable possibilities.
The change in technology from 5G to 6G, the expected uses and advantages of 6G, and how this next-generation network will transform daily life will all be discussed in this blog.
What’s New in 5G, and Why It Matters
With the speed up to 100 times faster than the 4G networks, 5G has begun to become largely available worldwide. This speed boost has made it possible to use programs like:
- Ultra-high-definition streaming and gaming: Along with improved mobile gaming experiences, users can take benefit of buffer-free 4K and 8K video streaming.
- Real-time communications: Quick feedback in VR and AR experiences is made possible by low latency of 5G, which also facilitates higher quality video conferences.
- Smart cities and IoT expansion: Smart homes, public safety, and traffic all have connected sensors that are become more responsive and effective.
However, 6G promises an even bigger transformation than 5G, which has opened the way for improved connection.
Understanding 6G: What Is It and How Will It Work?
With quite significantly more rapid speeds and increased dependability, 6G will continue to expand on the framework established by 5G. 6G is expected to eventually reach the terahertz (THz) frequency range, with data transfer speeds up to 100 times faster than 5G and wait time as low as 1 millisecond or less, whereas 5G generally runs in the 3.5 GHz frequency range. New applications such as real-time holographic communication and more sophisticated AI-powered solutions will be made possible by 6G’s expanded capabilities.
Current 6G Status and Timeline:

With academic and governmental research groups guiding the way, along with major tech corporations like Samsung, Huawei, and Nokia, 6G is currently in the research and development stage. It is expected that 6G networks would become commercially available in 2030.
Key Features of 6G
Not only the is speed important in the 5G to 6G transition, but it also changes the way we use the technology:
- Higher Frequencies: Operates at terahertz frequencies, which makes it possible for future applications and quicker data transfer.
- Extreme Latency Reduction: Applications that require ultra-responsiveness will be made possible by the reduction of latency to close to zero.
- Improved Connectivity Density: The capabilities of IoT are improved by the capacity to support 100 devices per square meter.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: 6G, in comparison to 5G, will be enhanced with AI and ML algorithms to automatically manage the jobs.
Expected Applications of 6G Technology
The only benefit of the 6G transition is the faster internet and another is the opportunity to access game-changing apps that will change our everyday lives. 6G is expected to have a significant influence in the following important areas:
a) Enhanced Mobile and Immersive Experiences
Hyper-realistic experiences that are immersive will be possible with 6G, including augmented and virtual reality experiences that are unrecognizable from the real world and streaming media in 8K and 16K resolution on mobile devices. Often seen in science fiction, real-time 3D holographic communication has the potential to become a commonplace feature, enabling much more interesting interactions than video conversations now offer.
b) AI-Driven Personalization and Predictive Analytics
6G is going to enable AI systems to offer extremely personalized experiences with previously unobtainable data processing rates. AI might be used, for instance, by wearable technology in the healthcare industry to forecast possible problems and track health parameters in real time. AI may be used in smart homes to proactively regulate security, temperature, and lighting by analyzing user preferences and patterns.
c) The Evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT)
With the ability to handle billions of devices that connect and interact with comfort, 6G will contribute to the realization of the immense IoT. With real-time data analysis, smart cities could benefit from sensors to improve security, minimize pollution, and manage traffic. Every household item, including washing machines and refrigerators, may be linked to create a more automated and efficient space.
d) Revolutionizing Remote Work and Education
6G will allow immersive and engaging virtual meetings and collaboration tools of the highest standard. With the introduction of real-time 3D holographic telepresence, remote work may change and allow for a new degree of cooperation that approaches in-person interactions. With VR and AR, education might advance by providing students with remote, virtual field trips and hands-on lab experiences.
e) Precision Healthcare and Remote Surgery
6G’s reduced latency will enable remote medical procedures and operations using robotic tools that can be operated by experts from any location. With wearable technology that continuously analyzes vital signs and promptly notifies medical professionals of any problems, health monitoring might also become continuous and real-time.
The Societal Impact of 6G: Challenges and Considerations
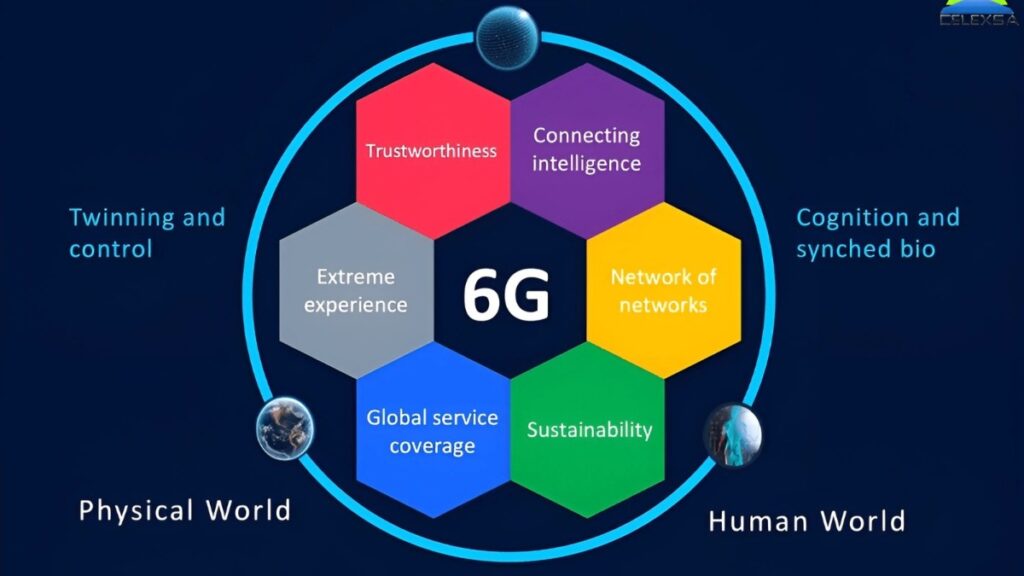
a) Privacy and Security Concerns
Privacy and data security issues will become increasingly important as 6G will make it possible to gather and analyze huge amounts of data in real-time. Stricter laws and improved security measures will be needed to safeguard user data and stop online attacks.
b) Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
There may be worries about the environmental impact of 6G because the infrastructure required to support it may require more energy. 6G technologies are anticipated to address this by emphasizing energy-efficient network design and integrating sustainability practices into network architecture and hardware.
c) Accessibility and Digital Divide
Accessibility is a challenge, just like any new technology. The digital gap must be addressed by the 6G deployment by making sure that underserved and rural communities are not left behind. In order to make 6G networks affordable and available to all, governments and businesses will need to collaborate.
Preparing for the 6G Future: What’s Next?

Countries including China, Japan, South Korea, and the United States are investing in 6G research and development, even if the technology is still in the research stage. To create a safe and effective 6G infrastructure, cooperation between governments, telecom carriers, and technology companies will be essential. With an emphasis on creating more robust, effective antennas and gadgets that can withstand terahertz frequencies, the race to 6G is also driving innovation in domains like materials science.
Challenges and Concerns with 6G
1. Infrastructure Development:
It will be quite expensive to build the infrastructure needed for 6G. With 6G, more base stations will be required because the ultra-high frequencies it uses have a restricted range.
2. Data Privacy and Security:
Concerns regarding cybersecurity and privacy are raised by the rise in data collection. Ensuring the security of personal data becomes increasingly important as 6G-enabled gadgets collect more of it. To safeguard user data, future laws and cybersecurity developments will be essential.
3. Environmental Impact:
The deployment of millions of base stations and devices will have an effect on the environment, even though 6G is anticipated to be energy-efficient. Developers and authorities will prioritize balancing 6G’s energy-saving features with its overall energy usage.
A Look Ahead: The Potential of 6G in 2030 and Beyond
With the anticipated widespread adoption of 6G networks by 2030, daily life will be completely different from what it is now. 6G-driven technology advancements are probably going to transform economies, redefine sectors, and alter how we engage with the outside world. The following is some of the glimpse that shows how our world could appear:
- Connected Transport: Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) connectivity will be supported by 6G, making autonomous cars more dependable and efficient. The widespread use of drones for delivery as well as fewer accidents and more energy-efficient traffic flow could result from this.
- Agricultural Advancements: Real-time crop and soil monitoring is one of the smart farming methods that 6G will make possible in agriculture. AI-powered autonomous devices with 6G connectivity may maximize water use, cut waste, and boost output.
- Space Exploration and Connectivity: A new era of satellite networks might be brought in by 6G, enabling internet access even in the most remote areas of the planet and perhaps allowing connectivity for missions to the moon and Mars.
- Enhanced Gaming and Entertainment: 6G has the potential to improve cloud-based gaming for gamers by providing multi-sensory experiences which combine haptic feedback with virtual and augmented reality, giving games a more lifelike feel.
Conclusion: 6G—Transforming Life as We Know It
The upcoming 6G technology is expected to be groundbreaking as 5G continues to enhance connection and mobile internet speeds. 6G networks have the potential to revolutionize everything from virtual business meetings that feel like in-person meetings to real-time health monitoring.
The transition from 5G to 6G is about more than just faster speeds; it’s about the future of belonging, when technology permeates and seamlessly integrates with everyday life. Although there are obstacles, such as infrastructure requirements and privacy issues, the potential rewards are immense and provide a glimpse of a future in which science fiction becomes a reality.
We are at the beginning of a new era of connectivity that will permanently change our world as we get ready for the launch of 6G, which will completely reorganize the digital landscape.
Read Also:- After BBA What Next? Best Careers For You || Top 10 Critical Emerging Challenges in Justice Delivery System

